The NIC Power Management in every Exchange Server should be disabled. It does not matter…
Exchange Server in DMZ or LAN network
Do you need to place the Microsoft Exchange Server in DMZ or LAN network? Do you want to know what the best practice is for Exchange in DMZ? In this article, you will learn if you should place an Exchange Server in DMZ or LAN network.
Table of contents
What is DMZ
In computer security, a DMZ or demilitarized zone (sometimes referred to as a perimeter network or screened subnet) is a physical or logical subnetwork. It contains and exposes an organization’s external-facing services to an untrusted, usually larger, network such as the Internet.
The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s local area network (LAN). An external network node can access only what is exposed in DMZ, while the rest of the organization’s network is firewalled.
The DMZ functions as a small, isolated network positioned between the Internet and the private network. If its design is effective, it will allow the organization extra time to detect and address breaches before they would further penetrate into the internal networks.
Exchange Server in DMZ or LAN network
When installing Exchange Server, you can install one of the two roles:
- Exchange Mailbox server role
- Exchange Edge Transport server role
Every Exchange role functions for a different purpose, whether a Mailbox role or an Edge Transport role. That’s why you need to follow the best practice, which is to place the:
- Exchange Mailbox server in the LAN network
- Exchange Edge Transport server in the DMZ network
Both Exchange server roles need different network ports to get the mail flow working (more on that below).
Important: Do not restrict the network traffic between internal Exchange servers. This means between internal Exchange servers and internal Lync or Skype for Business servers. Between internal Exchange servers and internal Active Directory domain controllers in any and all types of topologies. If you have firewalls or network devices that could potentially restrict or alter this kind of network traffic, you need to configure rules that allow free and unrestricted communication between these servers. Rules that allow incoming and outgoing network traffic on any port, including random RPC ports.
Exchange Mailbox server role in LAN
Microsoft recommends that you place the Exchange Mailbox server role in the LAN network. Place it in the LAN network because the Exchange Mailbox server needs communication to the Active Directory (AD). Most of the Exchange information is stored in AD.
Don’t move the Exchange Mailbox server to the DMZ network. If you do that, it will lose the communication to the domain controllers on the private LAN. As a result, the Exchange Mailbox server will not function. Instead, keep the Exchange Mailbox server next to your Domain Controllers in the LAN network.
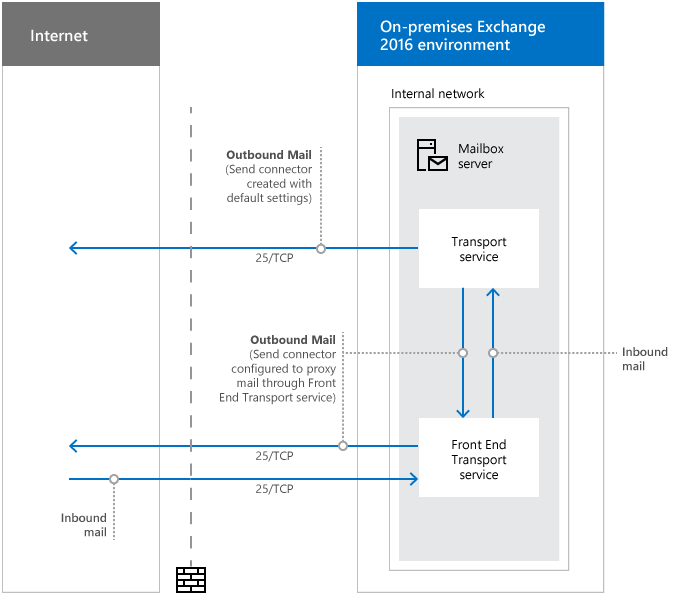
Network ports required for mail flow with Mailbox servers
It’s important to open the following ports if you have an Exchange Mailbox server.
| Purpose | Ports | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound mail | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Internet (any) | Mailbox server |
| Outbound mail | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Mailbox server | Internet (any) |
| Outbound mail (if proxied through the Front End Transport service) | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Mailbox server | Internet (any) |
| DNS for name resolution of the next mail hop* | 53/UDP,53/TCP (DNS) | Mailbox server | DNS server |
*DNS resolution of the next mail hop is a fundamental part of mail flow in any Exchange organization. Exchange servers that are responsible for receiving inbound mail or delivering outbound mail must be able to resolve both internal and external hostnames for proper mail routing. And all internal Exchange servers must be able to resolve internal hostnames for proper mail routing. There are many different ways to design a DNS infrastructure, but the important result is to ensure name resolution for the next hop is working properly for all of your Exchange servers.
Exchange Edge Transport server role in DMZ
Microsoft recommends that you place the Exchange Edge Transport server in DMZ network. Place it in a perimeter network that’s outside of your organization’s internal Active Directory forest.
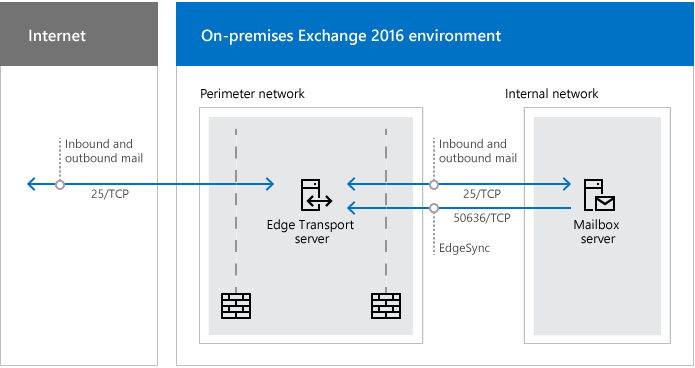
Edge Transport servers are almost always located in a perimeter network, so it’s expected that you’ll restrict network traffic between the Edge Transport server and the internet. Also, between the Edge Transport server and your internal Exchange organization. These network ports are described down below.
Network ports required for mail flow with Edge Transport servers
It’s important to open the following ports if you have an Exchange Edge Transport server.
| Purpose | Ports | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound mail – Internet to Edge Transport server | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Internet (any) | Edge Transport server |
| Inbound mail – Edge Transport server to internal Exchange organization | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Edge Transport server | Mailbox servers in the subscribed Active Directory site |
| Outbound mail – Internal Exchange organization to Edge Transport server | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Mailbox servers in the subscribed Active Directory site | Edge Transport server |
| Outbound mail – Edge Transport server to internet | 25/TCP (SMTP) | Edge Transport server | Internet (any) |
| EdgeSync synchronization | 50636/TCP (secure LDAP) | Mailbox servers in the subscribed Active Directory site that participate in EdgeSync synchronization | Edge Transport servers |
| DNS for name resolution of the next mail hop* | 53/UDP,53/TCP (DNS) | Edge Transport server | DNS server |
*DNS resolution of the next mail hop is a fundamental part of mail flow in any Exchange organization. Exchange servers that are responsible for receiving inbound mail or delivering outbound mail must be able to resolve both internal and external hostnames for proper mail routing. And all internal Exchange servers must be able to resolve internal hostnames for proper mail routing. There are many different ways to design a DNS infrastructure, but the important result is to ensure name resolution for the next hop is working properly for all of your Exchange servers.
Read more: Exchange firewall ports for mail flow and clients »
Conclusion
You learned the best practice for placing an Exchange Server in DMZ or LAN network. The only Exchange role Microsoft will support in a DMZ is the Edge Transport role. Everything else has to be in the internal network (LAN).
Did you enjoy this article? If so, you may like the article Find Exchange Server URLs with PowerShell. Don’t forget to follow us and share this article.



I always visit your website and follow your advice. Thanks Ali.
Hi Mr. Tajran
I tried to install the Exchange Edge Transport Role in windows server core 2019. As you know , we need to install Active Directory Lightweight Directory . So , I couldn’t install LDS on windows server core 2019 in my Lab and nothing find to help me . Do you have any idea?
Thank you
We are a small company (20 Users) and have 2 Windows Server VMs:
* DC and File Server [LAN]
* Exchange [DMZ]
While best practice is to have only the Edge Transport role within the DMZ, this doesn’t sound to be an option for those reasons:
* Exchange and then DC role should not be on the same host
* We need to be able to access Mailboxes from outside (via Outlook on Notebooks, phones as well as using OWA)
What should we do – if there’s anything we can do?
Thank you!
Tom
Well if something we learn lately is that OWA can be compromised and then everything that server has access too will be.
I put my exchange in a dmz, everything that comes in and out from that server (even to and from the lan) goes thru a firewall.
We took the time to analyze the traffic and we only give access to certain ips on 443 and 80. Not just allowing any 443 outgoing.
Is not the best but you can also use Malwarebites Firewall Control, isntall it and put in medium filter (learnign mode) and take the time to allow each IP that is needed for the correctly funtion of exchange. Use local DNS servers or fixed known like 8.8.8.8. Data could be sent out of a compromised server thru a dns tunnel too.