After renaming the Exchange database, we like to move the Exchange database to another drive.…
How to Create a Scheduled Task with PowerShell
Sometimes you want to configure a scheduled task for a PowerShell script. Let the PowerShell script run automatically in the background every hour or day. In our example, we like to create a scheduled task for the Health Checker PowerShell script. Suppose you want to create a scheduled task for another PowerShell script; the same steps will apply. In this article, you will learn how to create a scheduled task with PowerShell.
Table of contents
Before you start to create a scheduled task
Prepare the PowerShell script on the machine and create a service account with minimum privileges to run the script before you start creating a scheduled task.
Add script to folder
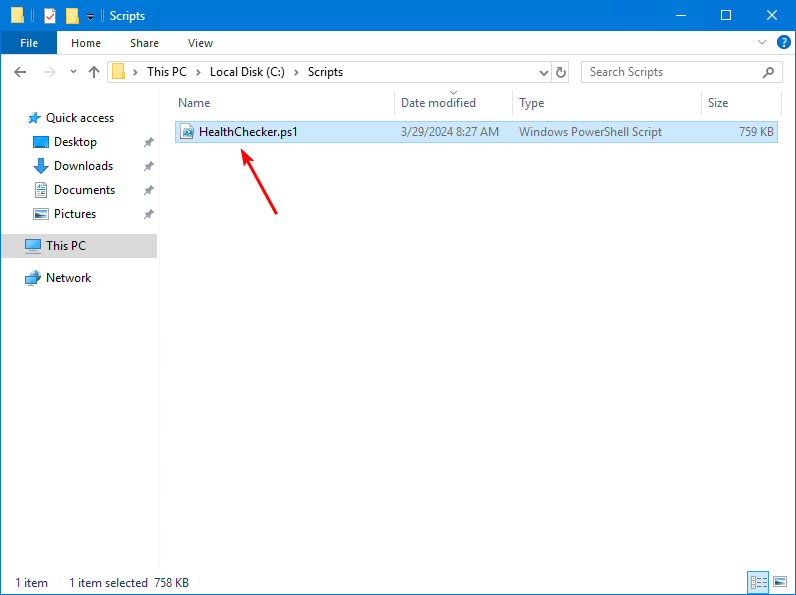
Create a Scripts folder on the (C:) drive. Place the PowerShell script in the C:\scripts folder.
In our example, it’s the PowerShell script HealthChecker.ps1.
Read more: Exchange Server health check with PowerShell script »
Create service account
It’s essential to create a service account with a strong password that will run the script.
In this example, we did create the service account svc-hc.
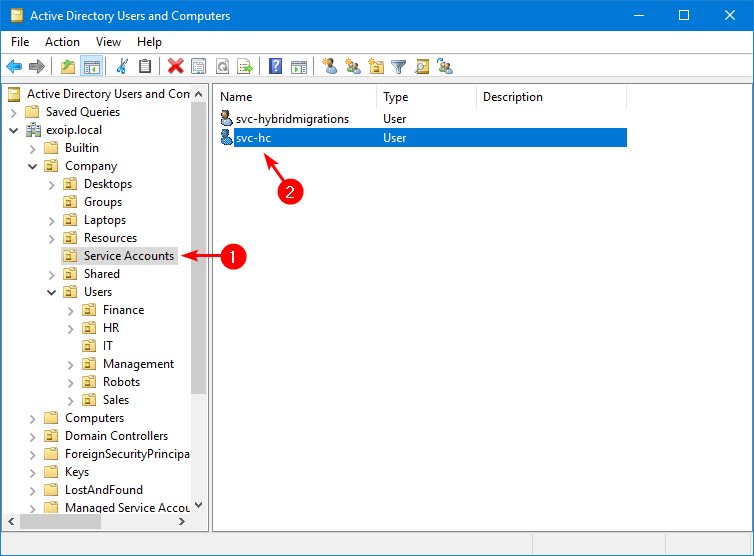
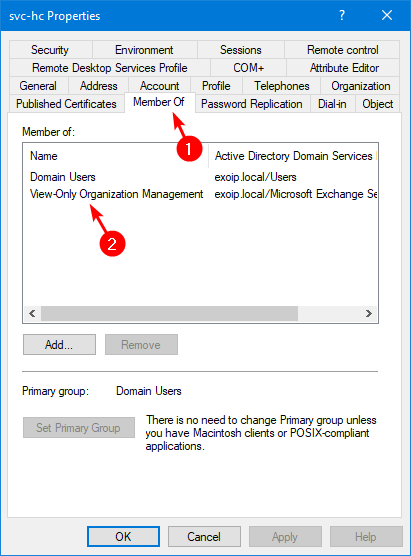
Add the user to the View-Only Organization Management.
Add service account to local administrators group
Add the service account to the local administrators group on each server that you want to run the PowerShell script against by following the below steps:
- Start Computer Management
- Click on Groups
- Double-click Administrators
- Add the service account svc-hc
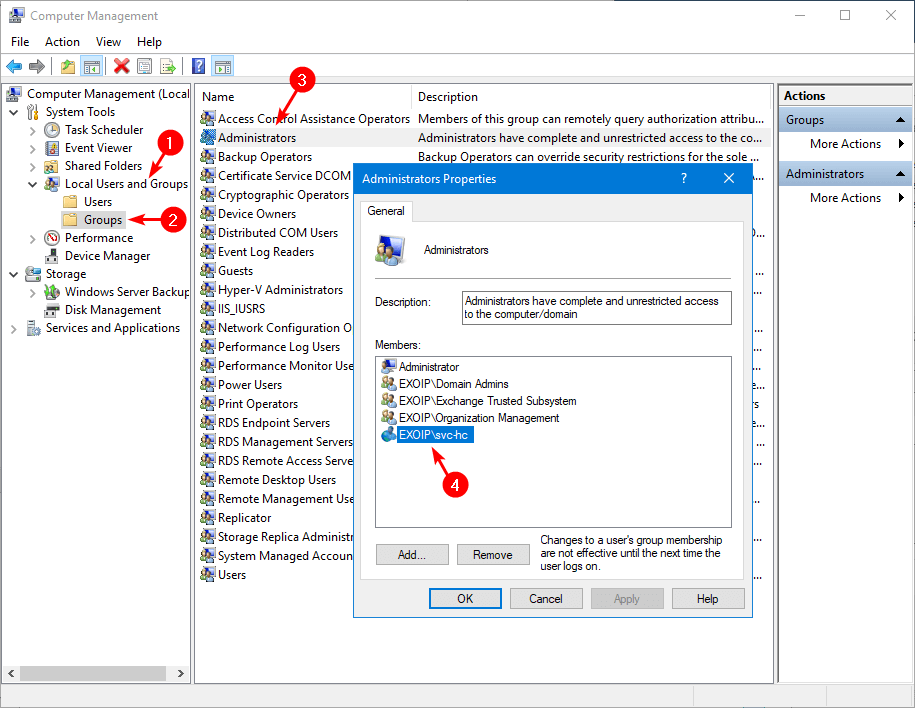
If you don’t add the service account to the local administrators group, the PowerShell script will not run.
How to create scheduled task with Powershell
To create a scheduled task with PowerShell, we will use the below cmdlets:
- New-ScheduledTaskTrigger
- New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet
- New-ScheduledTaskAction
- New-ScheduledTask
- Register-ScheduledTask
Note: Start Windows PowerShell as administrator and run the below commands.
Step 1. Create a scheduled task trigger object
Create a trigger that defines when the script should be executed.
Example 1. Daily at 2 AM.
$hcTrigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Daily -At 2amExample 2. Every four weeks on Monday at 2 AM.
$hcTrigger = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -Weekly -WeeksInterval 4 -DaysOfWeek Monday -At 2amStep 2. Create new scheduled task settings object
Create a new scheduled task settings object using the default settings.
$hcSettings = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSetStep 3. Create scheduled task action
Creates a scheduled task action and define the actions that need to execute.
Example 1. Update the HealthChecker script, execute the script against the local server, and generate the HTML report:
$hcAction = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute 'powershell.exe' -WorkingDirectory "C:\Scripts\" -Argument '-NonInteractive -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command ".\HealthChecker.ps1 -ScriptUpdateOnly; .\HealthChecker.ps1; .\HealthChecker.ps1 -BuildHtmlServersReport"'Example 2. Run the HealthChecker script against a remote Exchange server EX02-2019.
$hcAction = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute 'powershell.exe' -WorkingDirectory "C:\Scripts\" -Argument '-NonInteractive -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command ".\HealthChecker.ps1 -ScriptUpdateOnly; .\HealthChecker.ps1 -Server EX02-2019; .\HealthChecker.ps1 -BuildHtmlServersReport"'Step 4. Create scheduled task instance
Create a new scheduled task object using the pre-defined action, trigger, and settings objects:
$hcTask = New-ScheduledTask -Action $hcAction -Trigger $hcTrigger -Settings $hcSettingsStep 5. Register scheduled task definition on local computer
Create the scheduled task.
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName 'HealthChecker Daily Run' -InputObject $hcTask -User (Read-Host "Please enter username in format (Domain\Username)") -Password (Read-Host "Please enter password")The output shows the task name.
TaskPath TaskName State
-------- -------- -----
\ HealthChecker Daily Run ReadyRun scheduled task in Task Scheduler
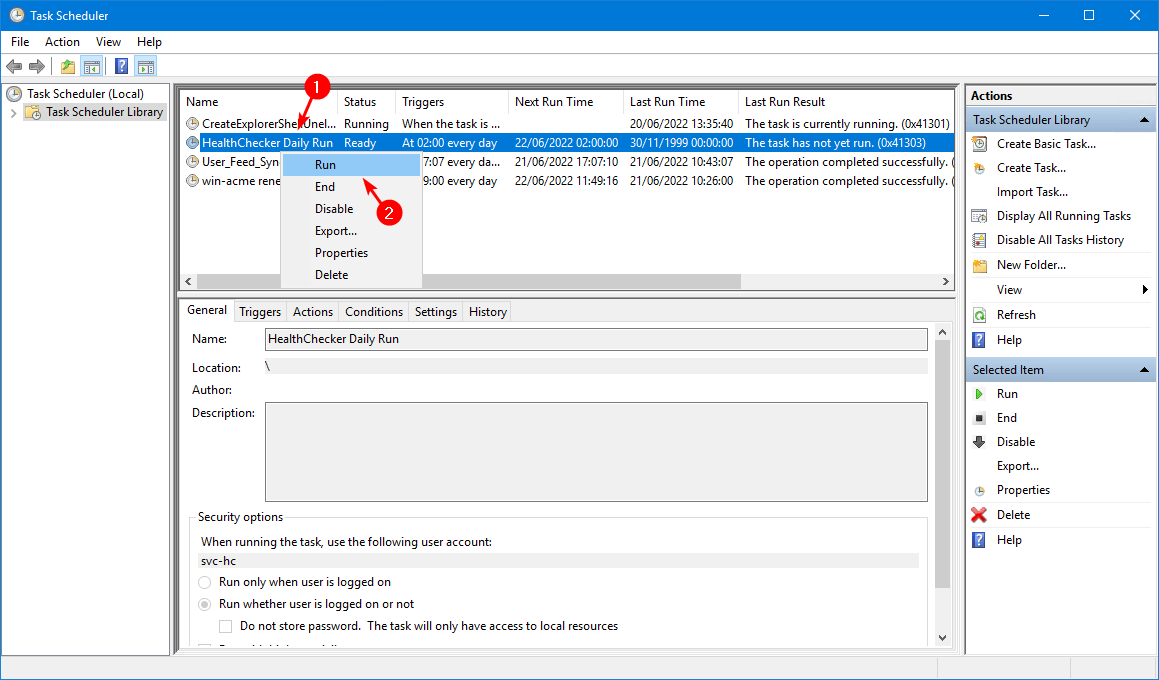
Always manually run a scheduled task to test that everything works:
- Start Task Scheduler
- Right-click the task
- Click on Run
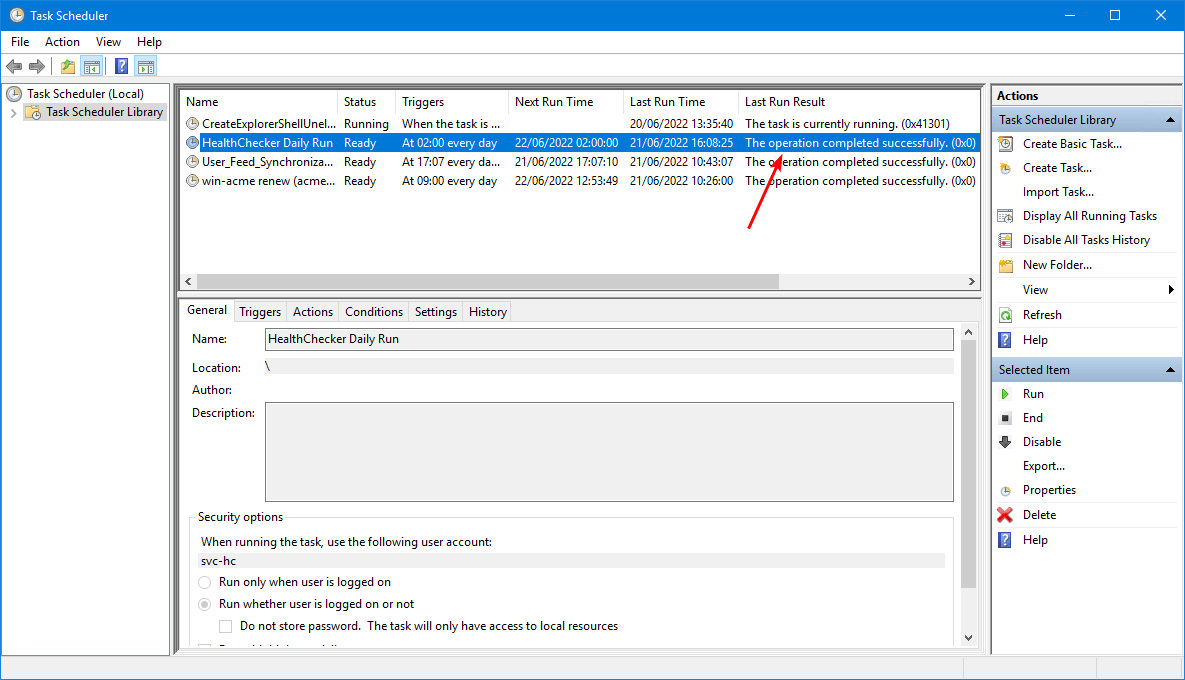
After the script finishes, it shows the last run result: The operation completed successfully. (0x0)
Do you want to export all the scheduled tasks? An excellent way to do this is with PowerShell. Read more in the article How to Export scheduled tasks with PowerShell.
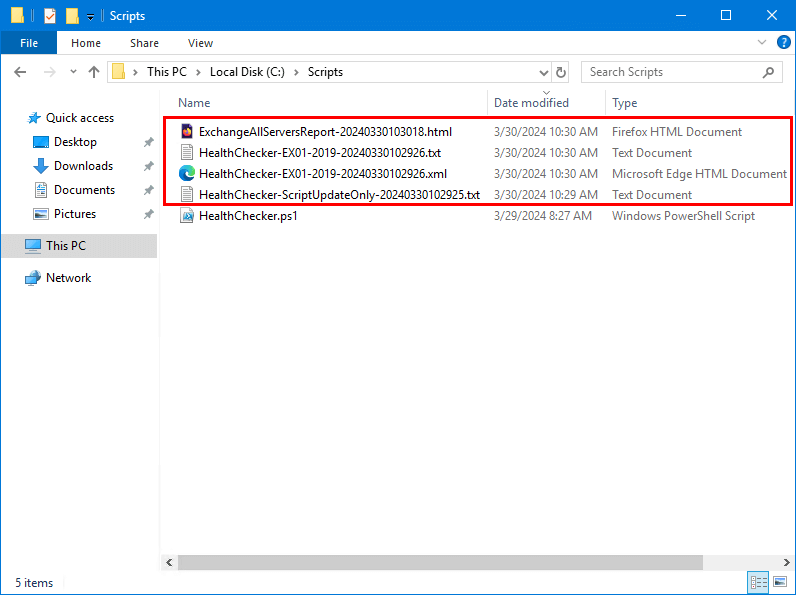
Verify PowerShell script report
Check that the PowerShell script successfully exported the results.
Did this help you to schedule a task with PowerShell on Windows?
Read more: Clear Windows Defender Antivirus exclusions with PowerShell »
Conclusion
You learned how to create a scheduled task with PowerShell. First, create a service account and make it a member of the view-only organization management group. The next step is to add the service account to the local administrator group. As of last, run the commands to create a new scheduled task. Remember to manually run the scheduled task and verify your work.
Did you enjoy this article? You may also like Get Active Directory count with PowerShell. Don’t forget to follow us and share this article.



Thank you for this. Is it possible to send the report by e-mail as well?
Thanks for this Ali. Using the script to run the DisableRemote PowerShell script on the Exchange server. In Task Scheduler it runs successfully but does not create the reports. Any idea why this should be the case? Thanks again. Simon
The DisableRemotePS.ps1 PowerShell script, which is shown in the article Disable remote PowerShell for non-admins does not have a report. So it’s the expected results.
Super helpful! Thanks for sharing.